Scoliosis is a medical condition that causes the spine to curve to the side, resulting in an abnormal posture. While scoliosis itself does not typically cause back pain, it can lead to other issues that may result in low back pain.
In this article, we’ll explore scoliosis and its effects on low back pain, including causes, symptoms, and treatment options.
What is Scoliosis?
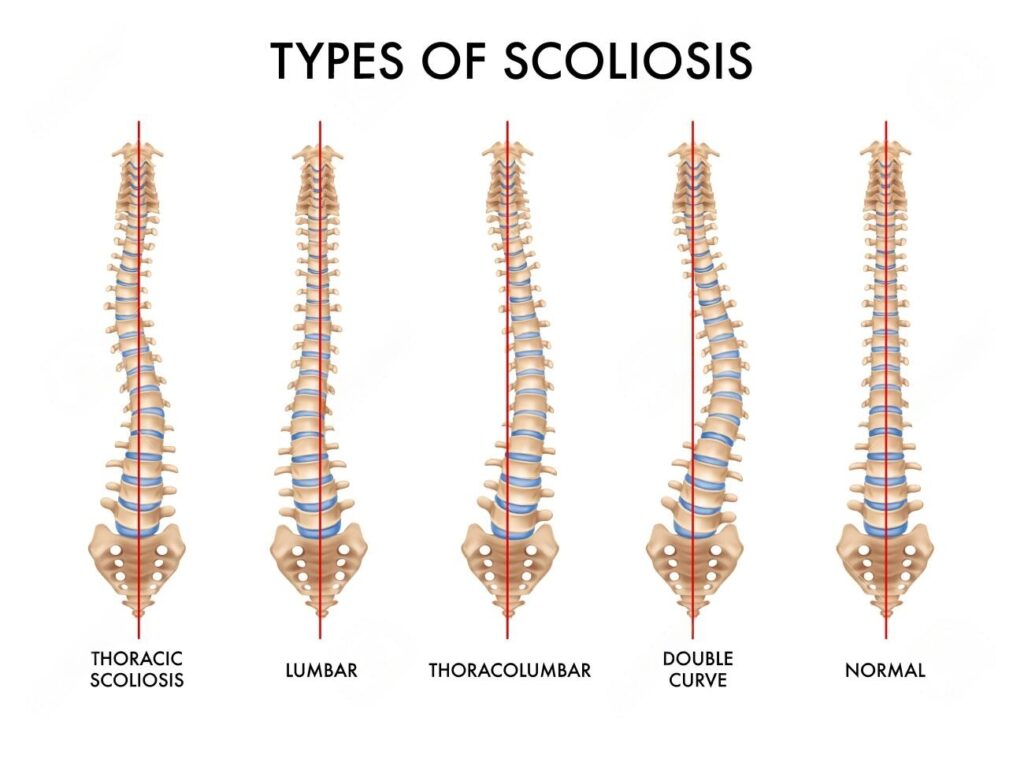
Scoliosis is a condition where the spine curves to the side, forming an “S” or “C” shape instead of the normal straight line. The condition can affect any part of the spine, from the neck to the lower back, but most often occurs in the thoracic (mid-back) or lumbar (lower back) regions.
Scoliosis can occur in children or adults and may be present at birth or develop later in life. The condition is usually diagnosed by X-ray, MRI, or physical examination.
How Does Scoliosis Cause Low Back Pain?
Scoliosis itself typically does not cause back pain. However, the abnormal curvature of the spine can lead to other issues that may result in low back pain. These issues may include:
- Muscle strain: As the spine curves, the muscles on one side may become stretched and weakened, while those on the other side become shortened and tight, leading to muscle imbalances and strain.
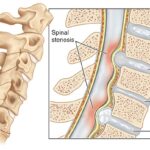
- Nerve compression: Severe scoliosis can cause nerve compression, resulting in pain, numbness, or tingling in the back, legs, or arms.
- Degenerative disc disease: Scoliosis can lead to degeneration of the discs in the spine, causing low back pain and stiffness.
Symptoms of Scoliosis-Related Low Back Pain
Symptoms of scoliosis-related low back pain may vary depending on the severity of the curvature and the underlying cause of the pain. Some common symptoms may include:
- Dull, aching pain in the lower back, usually on one side
- Muscle spasms or cramps
- Numbness or tingling in the legs or feet
- Difficulty standing up straight
- Uneven hips or shoulders
Treatment Options for Scoliosis-Related Low Back Pain
Treatment for scoliosis-related low back pain depends on the underlying cause of the pain and the severity of the curvature. Some common treatment options may include:
- Physical therapy: Strengthening and stretching exercises can help improve posture and relieve muscle imbalances.
- Pain medication: Over-the-counter or prescription pain medication can help manage low back pain.
- Surgery: In severe cases, surgery may be necessary to correct the curvature of the spine and relieve pressure on nerves.
Conclusion
While scoliosis itself typically does not cause low back pain, it can lead to other issues that may result in pain and discomfort. Understanding the symptoms and causes of scoliosis-related low back pain can help individuals seek appropriate treatment and manage their symptoms effectively.
FAQs
Can scoliosis cause other health problems besides low back pain?
Yes, scoliosis can cause other issues, such as breathing problems, digestive issues, or nerve damage.
Can scoliosis be prevented?
While there is no definitive way to prevent scoliosis, early detection and treatment can help manage the condition and prevent complications.
Is surgery the only treatment option for severe scoliosis?
No, surgery is not always necessary for severe scoliosis. Other treatment options, such as physical therapy or pain medication, may be effective in managing symptoms.
Can scoliosis worsen over time?
Yes, scoliosis can worsen over time if left untreated. Regular monitoring and treatment can help prevent the condition from progressing.
Can scoliosis worsen over time?
Yes, scoliosis can worsen over time if left untreated. Regular monitoring and treatment can help prevent the condition from progressing.