Back pain is a common complaint that can be caused by a variety of conditions. One of these conditions is spinal stenosis, which affects many people worldwide.
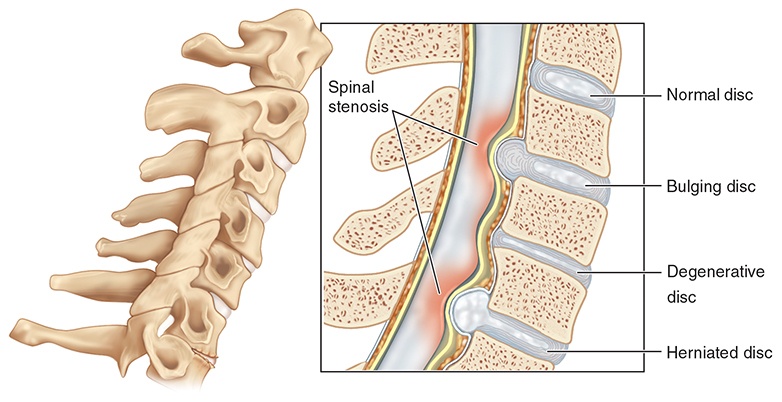
Spinal stenosis is a narrowing of the spinal canal, which can put pressure on the spinal cord and nerves, resulting in back pain and other symptoms.
In this article, we will discuss spinal stenosis, its causes, symptoms, and treatments, and how it affects back pain.
What is Spinal Stenosis?
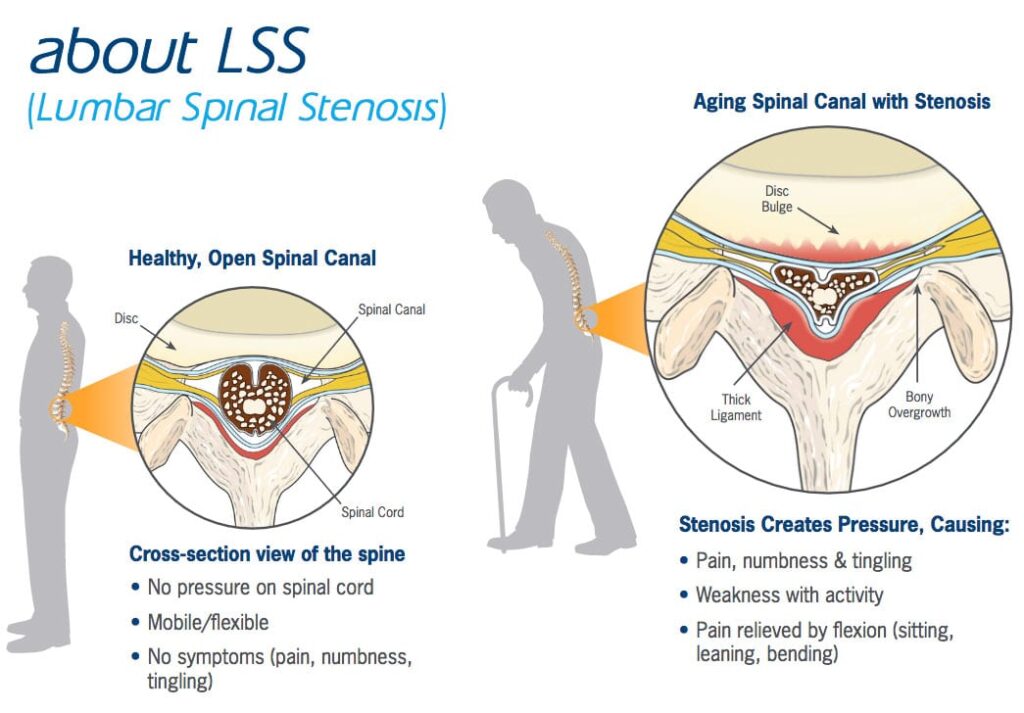
Spinal stenosis is a condition that occurs when the spinal canal narrows, putting pressure on the spinal cord and nerves. The spinal canal is a small, hollow space that runs through the center of the spine and contains the spinal cord and nerves.
When this space becomes too narrow, it can compress the nerves, causing pain, numbness, or weakness.
There are two main types of spinal stenosis: lumbar stenosis, which occurs in the lower back, and cervical stenosis, which occurs in the neck. Lumbar stenosis is more common and usually affects people over the age of 50.
Causes of Spinal Stenosis
Spinal stenosis can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
- Age-related changes
As we age, the ligaments and bones in the spine can thicken and harden, narrowing the spinal canal. - Herniated or bulging discs
A herniated or bulging disc can put pressure on the spinal cord or nerves, causing spinal stenosis. - Spinal injuries
Spinal injuries, such as fractures or dislocations, can cause spinal stenosis. - Tumors
Tumors can grow in the spinal canal and compress the nerves, causing spinal stenosis. - Genetic conditions
Some people are born with a smaller spinal canal, which can increase their risk of developing spinal stenosis.
Symptoms of Spinal Stenosis
The symptoms of spinal stenosis can vary depending on the location and severity of the condition. Common symptoms include:
- Back pain
Spinal stenosis can cause chronic or intermittent back pain, which may be accompanied by numbness or tingling sensations. - Leg or arm pain
If spinal stenosis is compressing the nerves in the lower back, it can cause pain, numbness, or weakness in the legs. If it occurs in the neck, it can cause pain, numbness, or weakness in the arms. - Bladder or bowel dysfunction
In severe cases of spinal stenosis, the nerves that control the bladder or bowel may be affected, causing incontinence or constipation.
Treatment of Spinal Stenosis
The treatment for spinal stenosis depends on the severity of the condition and the symptoms it is causing. Some treatment options include:
- Pain medication
Over-the-counter pain medications, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen, can help relieve mild to moderate back pain. - Physical therapy
Physical therapy can help strengthen the muscles in the back and improve flexibility, reducing pain and improving mobility. - Epidural steroid injections
Injections of steroids into the spine can help reduce inflammation and relieve pain. - Surgery
In severe cases of spinal stenosis, surgery may be necessary to remove the pressure on the spinal cord or nerves.
How Spinal Stenosis Affects Back Pain
intermittent back pain, which can be debilitating for some individuals. The pain may radiate down the legs or arms, making it difficult to stand or walk for extended periods.
Furthermore, spinal stenosis can cause muscle weakness, which can lead to poor posture and strain on the back muscles, exacerbating the pain.
Additionally, individuals with spinal stenosis may avoid physical activity due to the pain, leading to muscle atrophy and further weakness.
In summary, spinal stenosis can cause or contribute to back pain through nerve compression, muscle weakness, poor posture, and reduced physical activity.
Conclusion
Spinal stenosis is a common condition that affects many individuals worldwide. It occurs when the spinal canal narrows, putting pressure on the spinal cord and nerves, resulting in back pain and other symptoms.
Treatment options vary depending on the severity of the condition and may include pain medication, physical therapy, epidural steroid injections, or surgery.
Understanding spinal stenosis and how it affects back pain is crucial for individuals to seek appropriate treatment and manage their symptoms effectively.
FAQs
Can spinal stenosis be cured?
No, spinal stenosis cannot be cured, but treatment can help manage symptoms.
How is spinal stenosis diagnosed?
A doctor may use imaging tests, such as X-rays, MRI, or CT scans, to diagnose spinal stenosis.
Is spinal stenosis hereditary?
While there is no definitive evidence that spinal stenosis is hereditary, certain genetic conditions may increase the risk of developing the condition.
Can physical therapy help with spinal stenosis?
Yes, physical therapy can help strengthen the back muscles, improve flexibility, and reduce pain in individuals with spinal stenosis.
Is surgery the only option for severe spinal stenosis?
No, surgery is not always necessary for severe spinal stenosis. However, it may be recommended if other treatments have been ineffective in managing symptoms.