The human spine is naturally curved, but in some cases, the curvature can become more pronounced, leading to a condition called scoliosis. Scoliosis affects people of all ages, but it’s most commonly diagnosed in children and adolescents.
In this blog post, we’ll explore the different tests, exams, and imaging techniques used to diagnose scoliosis, and why early detection is so important.
What is Scoliosis?
Scoliosis is a condition where the spine curves to the side instead of remaining straight. The curvature can be mild, moderate, or severe, and it can develop in any part of the spine.
Some cases of scoliosis are congenital, while others develop due to factors like poor posture, muscle imbalances, or neuromuscular conditions.
Why is Early Diagnosis Important?
Early detection is important because it can help prevent scoliosis from progressing. If scoliosis is left untreated, it can cause problems like chronic pain, difficulty breathing, and decreased mobility.
When scoliosis is diagnosed early, treatment options like braces, physical therapy, and surgery can be more effective.
How is Scoliosis Diagnosed?
There are several tests, exams, and imaging techniques used to diagnose scoliosis. A doctor may use one or more of these methods to get an accurate diagnosis.
Physical Exam
There are several physical exams that doctors use to diagnose scoliosis. These include:
Forward Bend Test
During this test, the patient bends forward at the waist while the doctor observes the curvature of their spine. If the doctor notices a curve in the spine, they may order additional tests to confirm a diagnosis of scoliosis.
Adam’s Test
During this test, the patient stands with their feet together and bends forward at the waist with their arms hanging freely. The doctor observes the curvature of the patient’s spine and checks for any visible deformities, such as a rib hump.
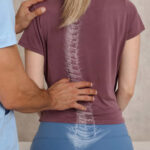
Rib Hump Measurement
During this test, the doctor measures the prominence of the ribs to see if there is a visible rib hump. A rib hump can be an indication of scoliosis.
Imaging Techniques
Imaging techniques are often used to confirm a diagnosis of scoliosis. The most common imaging techniques used for scoliosis diagnosis include:
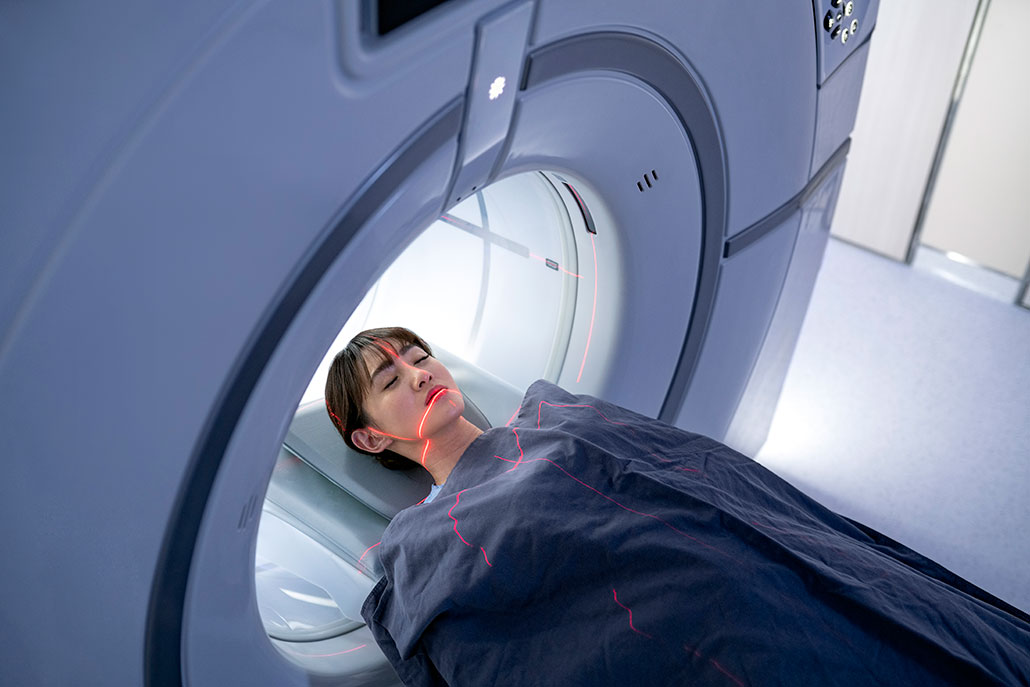
X-rays
X-rays are the most common imaging technique used to diagnose scoliosis. They can provide a detailed view of the spine and show the degree of curvature. During the x-ray, the patient will be asked to stand in different positions so that the healthcare professional can get a complete view of the spine. X-rays can also help identify any other abnormalities, such as fractures or tumors.
MRI
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is another imaging technique used to diagnose scoliosis. It is particularly useful in identifying any abnormalities in the spinal cord or nerves. An MRI uses a magnetic field and radio waves to create detailed images of the body. Unlike x-rays, MRIs do not use radiation.
CT Scan
A Computed Tomography (CT) scan is another imaging technique used to diagnose scoliosis. It uses a combination of x-rays and computer technology to create detailed images of the body. CT scans are particularly useful in identifying any abnormalities in the bones or joints of the spine. CT scans are often used when a doctor suspects a more complex spinal abnormality that may be causing scoliosis.
Bone Scan
A bone scan is a type of nuclear medicine imaging technique that can be used to diagnose scoliosis. During a bone scan, a small amount of radioactive material is injected into the patient’s bloodstream. The material then collects in areas of the body where there is increased bone activity, which can help identify any abnormalities in the spine.
Ultrasound
Ultrasound is another imaging technique that can be used to diagnose scoliosis. It is particularly useful in assessing the spine in infants and young children. During an ultrasound, high-frequency sound waves are used to create images of the body. Unlike x-rays and CT scans, ultrasounds do not use radiation.
Other Tests
In addition to physical exams and imaging techniques, doctors may also perform other tests to diagnose scoliosis. These tests include:
Neurological Exam
A neurological exam can help doctors identify any nerve or muscle problems that may be contributing to scoliosis.
Pulmonary Function Test
Scoliosis can sometimes cause breathing difficulties, so doctors may perform a pulmonary function test to evaluate lung function.
Genetic Testing
Some types of scoliosis are caused by genetic mutations, so genetic testing may be recommended in certain cases.
Conclusion
Diagnosing scoliosis involves a combination of physical exams, tests, and imaging techniques. Early diagnosis is important for effective treatment, so if you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of scoliosis, it is important to seek medical attention right away.
By working with a doctor and getting an accurate diagnosis, you can develop a treatment plan that will help you manage your condition and maintain a healthy, active lifestyle.
FAQs
What causes scoliosis?
The exact cause of scoliosis is unknown, but it can be related to genetics, neuromuscular conditions, or other underlying health issues.
How is scoliosis treated?
Treatment for scoliosis depends on the severity of the condition. Mild cases may only require monitoring, while more severe cases may require bracing or surgery.
Can scoliosis be prevented?
There is no known way to prevent scoliosis, but early detection and treatment can help prevent the condition from getting worse