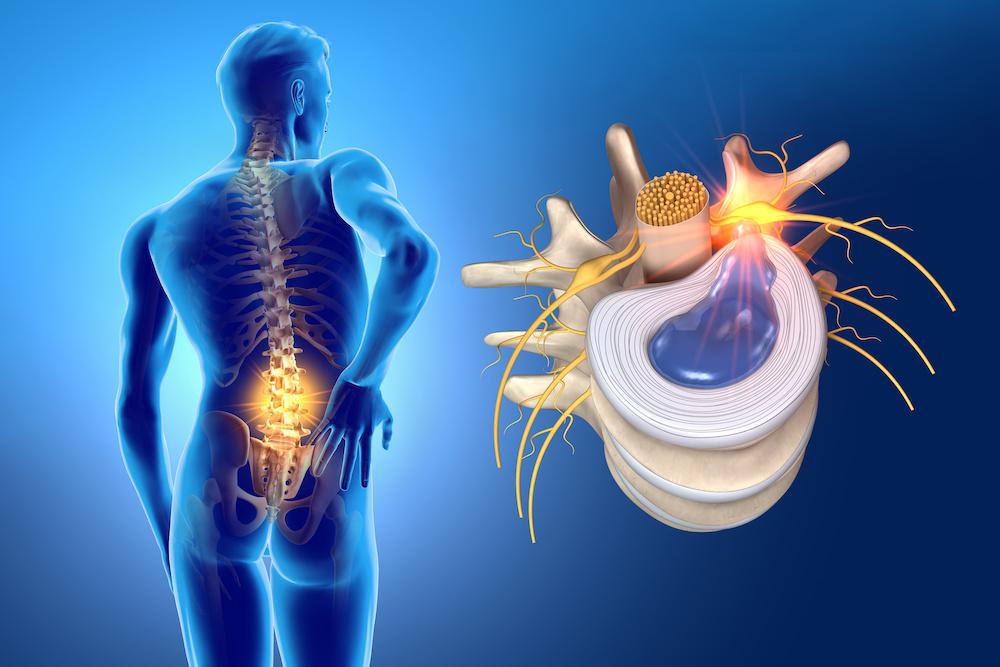
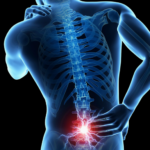
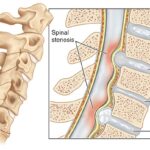
Back pain is a common complaint among many people, and one of the most common causes of this is a herniated disc. A herniated disc, also known as a slipped or ruptured disc, is a condition where the cushioning between the vertebrae in the spine pushes out of place and puts pressure on the surrounding nerves.
This can cause pain, numbness, tingling, and weakness in the lower back, legs, and feet. In this article, we will explore what a herniated disc is, how it causes low back pain, and what you can do to treat and prevent it.
What is a Herniated Disc?
A herniated disc occurs when the soft gel-like center of the disc, called the nucleus pulposus, pushes through a tear in the tough outer layer of the disc, called the annulus fibrosus. This can happen due to age-related wear and tear, or due to sudden injury or trauma.
When the herniated disc puts pressure on a nerve root, it can cause symptoms such as pain, numbness, tingling, and weakness in the lower back, legs, and feet.
Symptoms of a Herniated Disc
The symptoms of a herniated disc can vary depending on the location and severity of the condition. Some common symptoms include:
- Low back pain
- Leg pain
- Numbness or tingling in the legs or feet
- Weakness in the legs or feet
- Difficulty standing or sitting for long periods of time
- Shooting pain that radiates down one leg (sciatica)
Causes of a Herniated Disc
There are several factors that can increase your risk of developing a herniated disc, including:
- Age : As you get older, the discs in your spine become less flexible and more prone to injury.
- Genetics : Some people may have a genetic predisposition to developing herniated discs.
- Occupation : Jobs that require heavy lifting, bending, or twisting can put extra strain on your back and increase your risk of developing a herniated disc.
- Poor posture : Sitting or standing for long periods of time with poor posture can put extra pressure on your back and increase your risk of developing a herniated disc.
- Sudden injury or trauma : A sudden impact or injury, such as a car accident or sports injury, can cause a herniated disc.
Diagnosis of a Herniated Disc
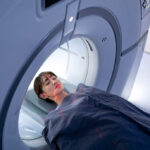
To diagnose a herniated disc, your doctor will perform a physical exam and ask you about your symptoms and medical history.
They may also order imaging tests such as an X-ray, MRI, or CT scan to get a better look at your spine and determine the location and severity of the herniation.
Treatment of a Herniated Disc
Treatment for a herniated disc depends on the location and severity of the condition, as well as the patient’s overall health and medical history. Some common treatment options include:
- Rest : Taking a break from strenuous activity and allowing your body to heal naturally can often help relieve symptoms.
- Physical therapy : Exercises and stretches designed to strengthen the back and core muscles can help alleviate pain and prevent future injury.
- Medication : Over-the-counter pain relievers or prescription medications may be recommended to manage pain and inflammation.
- Injections : Corticosteroid injections can help reduce inflammation and alleviate pain.
- Surgery : In severe cases where conservative treatment methods are not effective, surgery may be recommended to remove the herniated portion of the disc and alleviate pressure on the nerve root.
Prevention of a Herniated Disc:
While it may not be possible to completely prevent a herniated disc, there are several steps you can take to reduce your risk of developing this condition. These include:
- Maintaining a healthy weight : Excess weight puts extra strain on your back, increasing your risk of injury.
- Practicing good posture : Sitting and standing with proper posture can help alleviate pressure on your back and prevent injury.
- Using proper lifting techniques : When lifting heavy objects, bend at the knees and use your leg muscles to lift, rather than putting strain on your back.
- Staying active : Regular exercise and physical activity can help strengthen your back muscles and reduce your risk of injury.
- Avoiding smoking : Smoking can increase your risk of developing a herniated disc, as it reduces blood flow and oxygen to the discs in your spine.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the difference between a bulging disc and a herniated disc?
A bulging disc occurs when the disc protrudes out of its normal space between the vertebrae, while a herniated disc occurs when the inner gel-like material of the disc leaks out through a tear in the outer layer.
Can a herniated disc heal on its own?
In some cases, a herniated disc can heal on its own with rest and conservative treatment. However, in more severe cases, surgery may be necessary.
How long does it take to recover from a herniated disc?
Recovery time can vary depending on the severity of the condition and the treatment method used. In some cases, symptoms may resolve within a few weeks, while in others, it may take several months.
Conclusion
A herniated disc is a common cause of low back pain that can be caused by age-related wear and tear, sudden injury or trauma, and other factors.
Symptoms of a herniated disc can vary depending on the location and severity of the condition, but may include low back pain, leg pain, numbness or tingling, and weakness in the legs or feet.
Treatment for a herniated disc depends on the severity of the condition and may include rest, physical therapy, medication, injections, or surgery.
While it may not be possible to completely prevent a herniated disc, there are several steps you can take to reduce your risk of developing this condition, such as maintaining a healthy weight, practicing good posture, and staying active.
If you are experiencing low back pain or other symptoms of a herniated disc, it is important to speak with your doctor to determine the best course of treatment for your individual needs.